In the abstract, rest assured that a problem was solved.
SQL One Page
This one page presents points to bear in mind when entering a technical exam.
Concepts
SQL operates in a variety of environments, including the script engine of the underlying database, an IDE, or a specialised external tool for interacting with a database.
One table per modelled entity. An entity occurrence is once record.
An attribute is stored for an entity, and corresponds to a field. Ab attribute cab ibkt appear in one entity, unless it is the key attribute in another entity.
A relationship is established by a foreign key in one entity linking to the primary key in another.
Order of Precedence in SQL: When combining multiple logical operators, SQL follows a specific order of precedence to determine how conditions are evaluated:
- NOT (Highest precedence)
- AND
- OR (Lowest precedence)
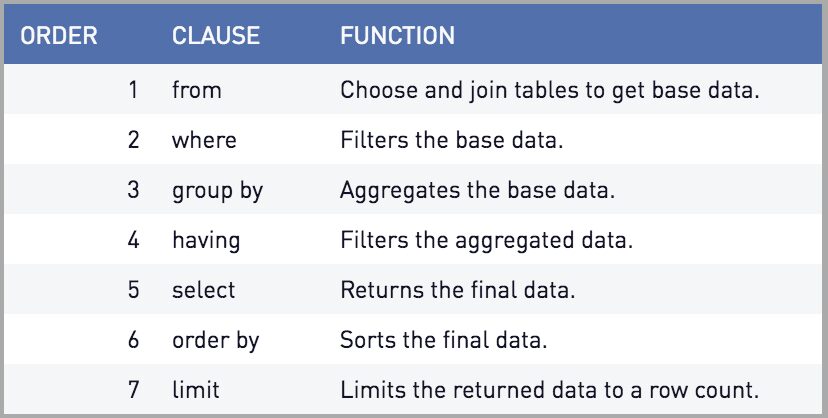
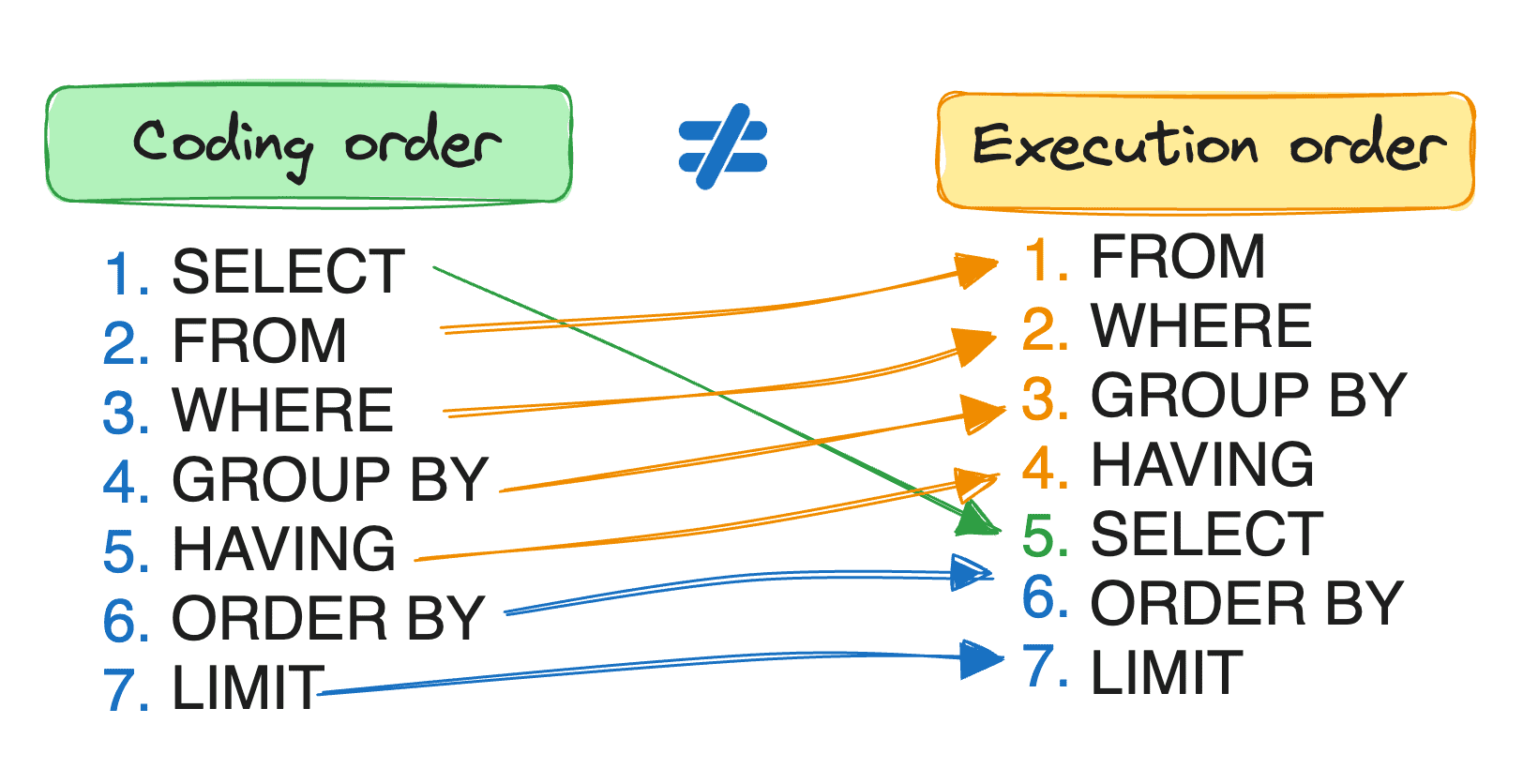
Order of Clauses
- SELECT
- FROM
- WHERE
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
- ORDER BY
Grouping Rules
- Every non-aggregate column that appears in the SELECT clause must also appear in the GROUP BY clause.
- You may not use aliases in the HAVING clause.
- You may use aliases in the ORDER BY clause.
- You may only use calculated fields in the HAVING clause.
- You may use calculated field aliases or actual fields in the ORDER BY clause.
Methods
CREATE TABLE EmployeeSalary (EmployeeID int, JobTitle varchar(50), Salary int ); INSERT INTO EmployeeDemographics VALUES (1001, 'Jim', 'Halpert', 30, 'Male');
SELECT TOP
SELECT TOP 5 * FROM Orders
HAVING
Condition the selection on values in columns.
SELECT JobTitle, AVG(Salary) AverageSalary
FROM EmployeeDemographics
JOIN EmployeeSalary
ON EmployeeDemographics.EmployeeID =
EmployeeSalary.EmployeeID
GROUP BY JobTitle
HAVING AVG(Salary) > 45000
ORDER BY AVG(Salary)
UPDATE
Make data changes to existing records.
UPDATE Students2 SET email = LOWER(CONCAT(FirstName, '.', LastName, '@CENITCOLLEGE.com'));
USE
Switch between databases from script.
USE db1; USE Northwind; SELECT * FROM Employees;
ALTER
ALTER TABLE Employees ADD PhoneNumber VARCHAR(15); -- Modifying a Column: ALTER TABLE Employees ALTER COLUMN Salary DECIMAL(12,2); -- Dropping a Column: ALTER TABLE Employees DROP COLUMN PhoneNumber; -- Dropping a Table DROP TABLE Employees;
Temp Tables
Valid until the end of the studio session.
CREATE TABLE #temp_Employee2 ( JobTitle varchar(50), EmployeesPerJob int, AvgAge int, AvgSalary int ); INSERT INTO #temp_Employee2 SELECT JobTitle, COUNT(JobTitle), AVG(Age), AVG(Salary) FROM EmployeeDemographics emp JOIN EmployeeSalary sal ON emp.EmployeeID = sal.EmployeeID GROUP BY JobTitle; SELECT * FROM #TEMP_EMPLOYEE2;
CTE
Common Table Expressions can be used multiple times within the subsequent query.
CREATE TABLE #temp_Employee2 ( JobTitle varchar(50), EmployeesPerJob int, AvgAge int, AvgSalary int ); INSERT INTO #temp_Employee2 SELECT JobTitle, COUNT(JobTitle), AVG(Age), AVG(Salary) FROM EmployeeDemographics emp JOIN EmployeeSalary sal ON emp.EmployeeID = sal.EmployeeID GROUP BY JobTitle; SELECT * FROM #TEMP_EMPLOYEE2;